ผลต่างระหว่างรุ่นของ "VC-SNDP:spider decomposition"
Jittat (คุย | มีส่วนร่วม) |
Jittat (คุย | มีส่วนร่วม) |
||
| แถว 50: | แถว 50: | ||
* path เหล่านั้น internally vertex disjoint, | * path เหล่านั้น internally vertex disjoint, | ||
* terminal ใน <math>T'</math> เป็นจุดปลายได้แค่ path เดียว | * terminal ใน <math>T'</math> เป็นจุดปลายได้แค่ path เดียว | ||
| + | |||
| + | อัลกอริทึมเป็นดังนี้ | ||
| + | |||
| + | # สุ่มลำดับ terminal ให้เป็น <math>t_1,t_2,\ldots,t_j</math> | ||
| + | # ให้ ''H'' เป็นกราฟว่าง | ||
| + | # พิจารณา <math>t=t_1,t_2,\ldots</math> | ||
| + | ## หา min-cost augmentation for <math>t</math> w.r.t. <math>T_{i-1}</math> เมื่อ <math>T_i=\{t_1,\ldots,t_i\}</math> | ||
== Reduction lemma == | == Reduction lemma == | ||
=== Proof of the spider decomposition with the reduction lemma === | === Proof of the spider decomposition with the reduction lemma === | ||
รุ่นแก้ไขเมื่อ 08:39, 25 กุมภาพันธ์ 2552
This page describes spider decompositions and the approach of Chuzhoy Khanna and Chekuri and Korula in tackling the single-source k sndp.
ให้กราฟ เซตของ terminals T และจำนวนเต็มบวก เรียกโหนดใน T ว่าเป็น black vertices, นอกจากนั้นเป็น white vertices.
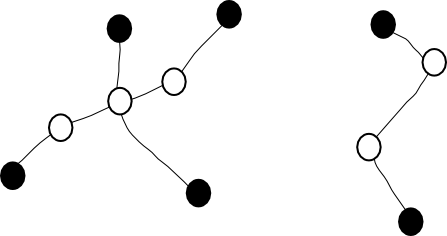
Spider คือ tree ที่มีโหนดที่มีดีกรีมากกว่าสองไม่เกิน 1 จุดยอด ถ้ามี vertex ดังกล่าว จะเรียกว่าเป็น head ถ้าไม่มี spider จะเป็น path และจะสามารถเรียกโหนดใดเป็น head ก็ได้; เรียกจุดยอดที่ไม่ใช่ leaf และ head ว่า intermediate vertex, เรียก leaf ว่า foot, เรียก path จาก head ไป leaf ว่า leg
เนื้อหา
Decomposition
Chuzhoy และ Khanna ได้ใช้ spider decomposition ในการพิสูจน์ approximation algorithm สำหรับ ss-k-sndp อย่างไรก็ตามในที่นี้เราจะใช้ decomposition ที่ weak กว่าของ Chekuri และ Korula
Chekuri-Korula [Theorem 4.4] แสดงว่า ให้กราฟ G ที่ทุก ๆ คู่ของจุดยอดสีดำ k-element connected, มีสับกราฟ H ของ G ที่สามารถ partition เป็น spiders ที่
- ทุก ๆ leaf เป็น black vertex และ ทุก ๆ intermediate vertex เป็น white vertex (สังเกตว่า head เป็น black vertex ได้)
- ทุก ๆ black vertex เป็น foot ของ k spiders พอดี, และ ทุก ๆ white vertex อยู่ใน 1 spider เท่านั้น
- สำหรับกรณีที่ spider มี white vertex เป็น head จะต้องมี leg อย่างน้อย 2 legs
ด้านล่างแสดงตัวอย่างของ spiders
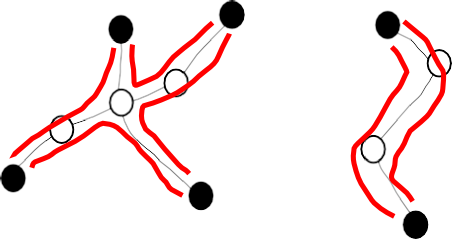
spider decomposition กับ set ของ paths
พิจารณา spider แต่ละตัว เราจะพบว่าเราสามารถหาเซตของ path จากแต่ละ foot หนึ่ง ๆ ไปยังอีก foot ใด ๆ ได้ โดยที่ค่าใช้จ่ายรวมไม่เกิน 2 เท่าของ cost ของ spider (ดูรูป)
ดังนั้น ถ้าเรามี spider decomposition เราจะได้ว่าเราสามารถหา, สำหรับทุก ๆ terminal , set of internally vertex disjoint paths ที่ เพราะว่า
- สังเกตว่า white vertex ไม่ share กันระหว่าง spider
- ทุก ๆ black vertex เป็น leg ของ k spiders (ดังนั้นดึงมาตัวละ path)
ด้านบนคือหัวใจของบทพิสูจน์ของ Lemma 4.3 ใน Chekuri-Korula
บทพิสูจน์: มี spider decomposition
ส่วนนี้จะมาเขียนทีหลัง
โดย induction บนจำนวน edge ระหว่าง white vertices ใน G ใน base case ให้กราฟ G ไม่มี edge ดังกล่าวเลย จะได้ว่า G เป็น bipartite. ( edge ระหว่าง black vertices ก็ไม่มีด้วย) เนื่องจากแต่ละคู่ของ black vertices เป็น k-element connected แสดงว่าแต่ละ black vertex จะต้องมีอย่างน้อย k white vertices ที่ติดกับมัน
เราจะสร้าง set of spiders โดยให้แต่ละโหนด b
Approximating SS-k-VC-SNDP
ในส่วนนี้จะอธิบายอัลกอริทึมตามที่ปรากฎใน Chekuri-Korula
ให้กราฟ เซตของ terminals และ root
สำหรับสับเซตของ terminals ใด ๆ และ terminal , เราจะกล่าวว่า เซตของ paths เป็น augmentation for w.r.t. ถ้า
- path เริ่มที่ t ไปถึงโหนดใน
- path เหล่านั้น internally vertex disjoint,
- terminal ใน เป็นจุดปลายได้แค่ path เดียว
อัลกอริทึมเป็นดังนี้
- สุ่มลำดับ terminal ให้เป็น
- ให้ H เป็นกราฟว่าง
- พิจารณา
- หา min-cost augmentation for w.r.t. เมื่อ