ผลต่างระหว่างรุ่นของ "204512-53/lecture8"
KenMay (คุย | มีส่วนร่วม) |
|||
| แถว 10: | แถว 10: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Network flow problem= | ||
| + | |||
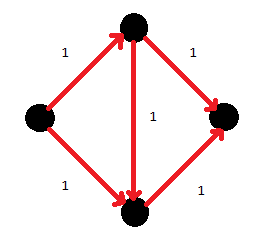
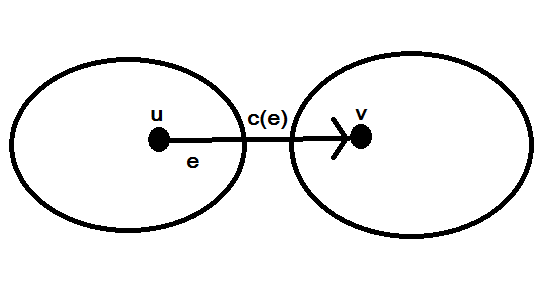
| + | In graph theory, a flow network is a directed graph where each edge has a capacity and each edge receives a flow. The amount of flow on an edge cannot exceed the capacity of the edge. Often in Operations Research, a directed graph is called a network, the vertices are called nodes and the edges are called arcs. A flow must satisfy the restriction that the amount of flow into a node equals the amount of flow out of it, except when it is a source, which has more outgoing flow, or sink, which has more incoming flow. A network can be used to model traffic in a road system, fluids in pipes, currents in an electrical circuit, or anything similar in which something travels through a network of nodes. | ||
=Maximum flow problem= | =Maximum flow problem= | ||
รุ่นแก้ไขเมื่อ 06:41, 24 กันยายน 2553
บันทึกคำบรรยายวิชา 204512-53 นี้ เป็นบันทึกที่นิสิตเขียนขึ้น เนื้อหาโดยมากยังไม่ผ่านการตรวจสอบอย่างละเอียด การนำไปใช้ควรระมัดระวัง
Algorithm Lecture #8 จดบันทึกคำบรรยายโดย:
นาย บดินทร์ แสงทองล้วน 5314550113
นาย วิชา มีสุขสบาย 5314550164
นาย อภิชาติ ทวีศิริเวทย์ 5314550199
เนื้อหา
Network flow problem
In graph theory, a flow network is a directed graph where each edge has a capacity and each edge receives a flow. The amount of flow on an edge cannot exceed the capacity of the edge. Often in Operations Research, a directed graph is called a network, the vertices are called nodes and the edges are called arcs. A flow must satisfy the restriction that the amount of flow into a node equals the amount of flow out of it, except when it is a source, which has more outgoing flow, or sink, which has more incoming flow. A network can be used to model traffic in a road system, fluids in pipes, currents in an electrical circuit, or anything similar in which something travels through a network of nodes.
Maximum flow problem
Maximum flow problem: ปัญหาการหาปริมาณการไหลสูงสุด ซึ่งเป็นหนึ่งในปัญหาเน็ตเวิร์คโฟล์วที่น่าสนใจ
สัญลักษณ์ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
G คือ กราฟที่เราสนใจ
G = (V,E) คือ ฟังก์ชั่นของกราฟ G โดยที่ V คือ เซตของโหนด และ E คือเซตของเส้นเชื่อม
C: E->R+ คือ Capacity ของเส้นเชื่อม เซตจำนวนจริงบวกไม่รวมศูนย์ (0, +∞)
s-t คือ เซตของเส้นทางจาก s ไปถึง t
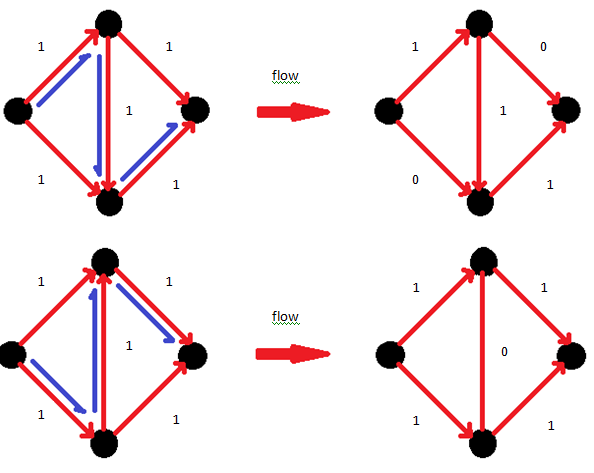
Maximum flow คือโจทย์หนึ่งของเน็ตเวิร์คโฟล์วโจทย์นี้ต้องการหาค่ามากที่สุดของโฟล์ว จากต้นทาง(s) ที่ส่งได้ไม่เกินความจุของเส้นเชื่อม(u) แต่ละเส้น เพื่อให้ได้ค่ารวมมากที่สุดจากต้นจนถึงปลายทาง (t)
Classic problem
Maximum flow คือเท่าไหร่ : ต้องหา path มาเรื่อยๆ จนไม่มี path
ถ้าได้รูปแบบข้างต้นก็ไม่มีปัญหา แต่ถ้าเกิดได้แบบ
จะกลายเป็นปัญหา แล้วจะแก้ไขอย่างไร?
แนวคิด
Algorithm
- F <- 0
- G(f) เป็น residual graph ของ f
- ถ้ามี path จาก s ไป t ใน G(f)
- P <- path จาก s ไป t ใน G(f)
- C <- capacity ต่ำสุดของเส้นเชื่อมใน path P
- Update f ด้วย flow path P ด้วยปริมาตร C
- หา G(f) <- residual graph ของ flow f
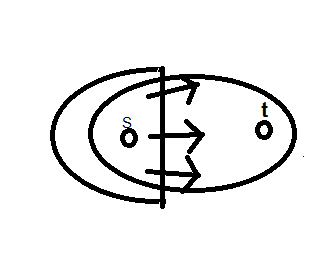
st-cut
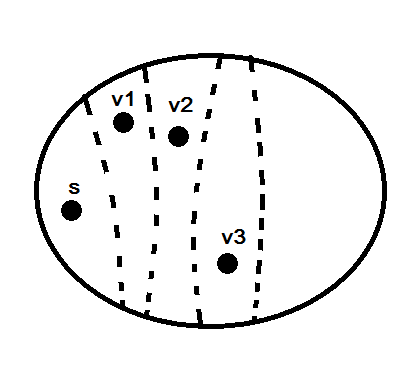
พิจารณา sub set ของ node กลุ่มหนึ่ง
ถ้า จะเรียก ว่า st-cut ;
cut ที่ตัด s กับ t ออกจากกัน
เราสนใจ edge ทั้งหมดที่ข้ามจาก s ไป t
1) นิยาม
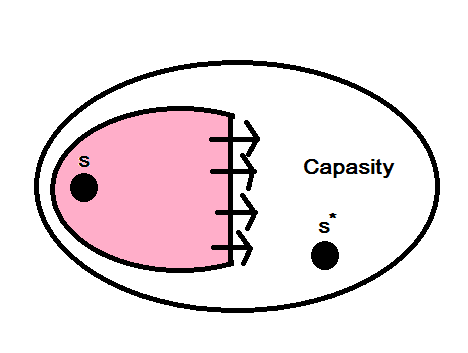
Flow ใดๆเราพิจารณาการส่ง volumeจาก s ไป t
ถ้าเราพิจารณา volume ที่วิ่งผ่าน cut ต้องเท่ากับ volume ที่ออกจาก S
2) นิยาม
; flow ที่วิ่งจาก ทั้งหมดเลย
flow สามารถวิ่งไปและวิ่่งกลับได้
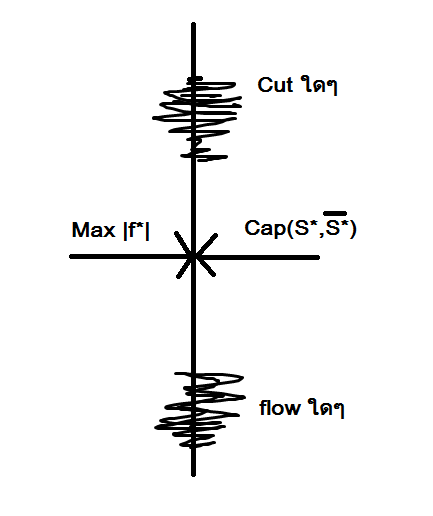
สำหรับ st-cut ใดๆ เราได้ว่า
เราจะพิสูจน์
คือ Volume ของ f
พิสูจน์
สำหรับ st-cut S ใดๆ
พิสูจน์
สำหรับทุกๆ
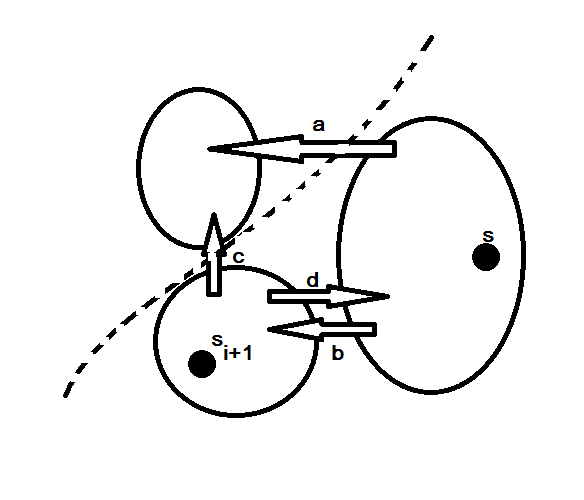
พิสูจน์ โดย Induction ตั้งแต่ 0 ถึง k
เป็น base case ซึ่งจะเท่ากันตามนิยาม
เราจะพิสูจน์ว่า
ได้ มี flow ที่วิ่งเข้าวิ่งออกของ c กับ d สุดท้ายรวม flow เส้นปะเข้า
ไปเราได้ว่า
เนื่องจากเรารู้ว่า
Claim(1)
Claim(2)
Ford-Fullerson
สำหรับ st-cut ใดๆ
เราพิจารณา flow มีขนาดเท่ากับ cut ใดๆ แปลว่า flow นั้นมีขนาดใหญ่สุด
เราสามารถพิสูจน์ต่อได้ว่า flow ที่มีขนาดเท่ากับ เราจะได้ flow ที่มีขนาดใหญ่ที่สุด
พิสูจน์ว่า
flow f ที่ out-put โดย Ford-Fullerson เป็น maximum flow
หา s-t cut ที่
เราต้องการ
พิสูจน์
1) flowต้องเต็ม
2) edgeที่วิ่งกลับต้องไม่มีflowเลย
เราพิสูจน์โดย By Contradition
พิจารณา e=(u,v) ที่
Claim
ถ้าไม่เท่ากัน flow จะไม่เต็ม เท่ากับว่ามี path อีก 1 path ใน residual graph เพราะฉะนั้น เป็นจริง
สิ่งที่เราได้นอกจากจะได้ max flow เราจะได้ min cut เพราะ max flow = min cap
เวลาในการทำงาน
ความคืบหน้าของมันคือจำนวน |f| เพิ่มขึ้นเรื่อยๆ แต่ต้องมันใจว่าไปถึง max flow ไม่ใช่เพิ่มขึ้นน้อยลงเรื่อยก็ไม่มีทางไปถึง
m คือจำนวน edge, n คือ จำนวน node; ทำทั่วไป ; หา path ;
ถ้า Capacity เป็น integer จำนวนรอบที่ใช้จะเท่ากับจำนวนของ max flow
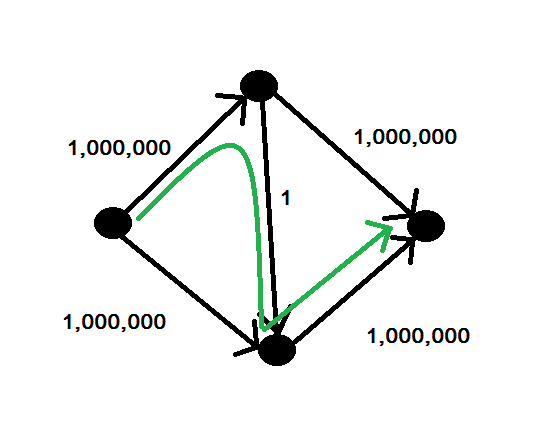
ตัวอย่างที่ Fold-Fullerson ล้มเหลว
Bipatite Matching
ปัญหาที่สามารถมองเป็น max flow ได้
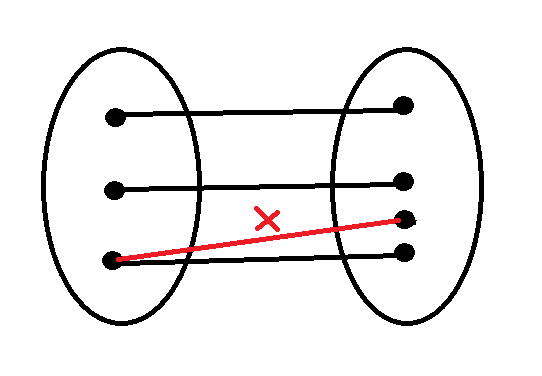
กราฟ G จะเรียกว่าเป็น Bipatite graph ถ้า set ของ vertex V สามารถแบ่งเป็น
A,B ที่
แล้วไม่มีเส้นเชื่อม (u,v) ที่ หรือ
เซต เรียกว่าเป็น matching ถ้าไม่มีโหนดใดๆ ติดกับเส้นเชื่อม M เกิน 1 เส้น
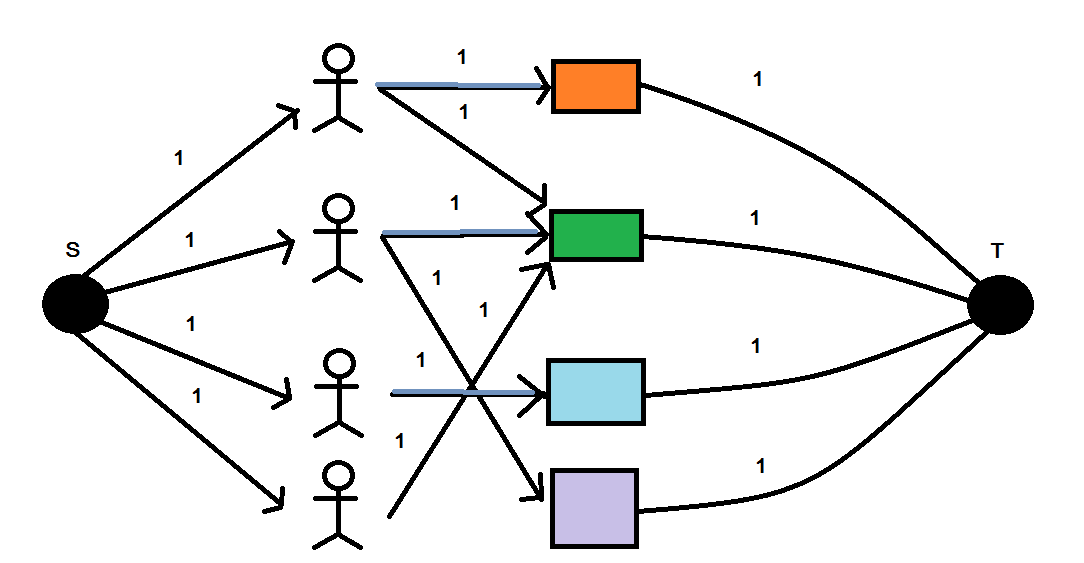
ปัญหา Bipartite Matching
สมมุติว่า มีคน n คน ซื้อกับข้าว n ห่อ เส้นเชื่อมที่โยงไปคือ ที่สามารถกินข้าวห่อได้ ทำอย่างไรให้ทุกคนได้กินข้าวห่อ
สร้าง Supernode S กับSupernode T ใส่ทิศทางและ Capasity
หาคำตอบในกราฟนี้โดยใช้ maxflow จะ work ได้ maxflow ต้องเป็นจำนวนเต็ม